The Canadian dollar is one of the most traded currencies in the forex markets while the Canadian economy is export-driven and highly dependent on the US economy. How does this affect the Canadian dollar?
Drivers of the Canadian Dollar
Canada has a highly developed economy and boasts the ninth-largest economy in the world. This makes the Canadian dollar an attractive currency for forex traders and the US dollar/Canadian dollar is one of the most traded currency pairs. This article will examine the factors which have an impact on the value of the Canadian dollar.
The value of the Canadian dollar (CAD) is influenced by a variety of factors. Let’s take a look at the factors which can affect the Canadian dollar.
The Effect of Commodity Prices on the Canadian dollar
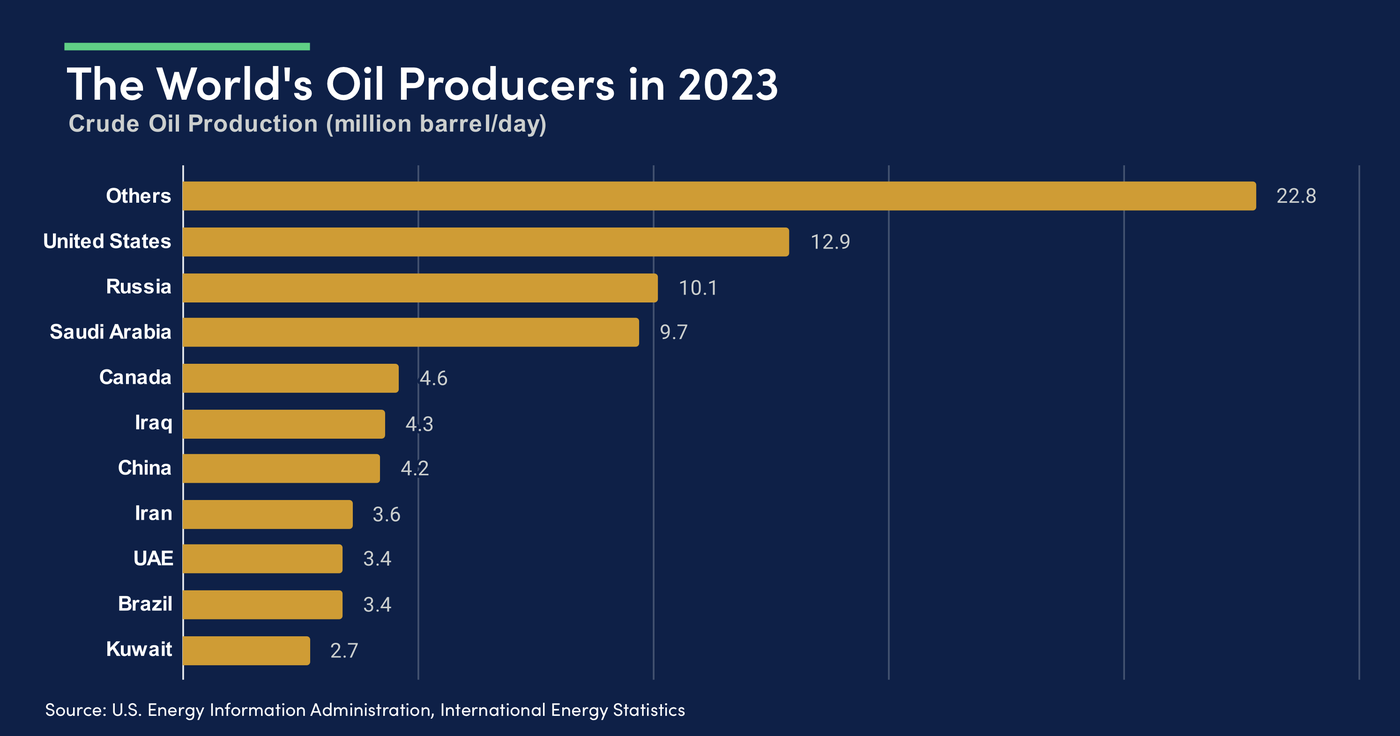
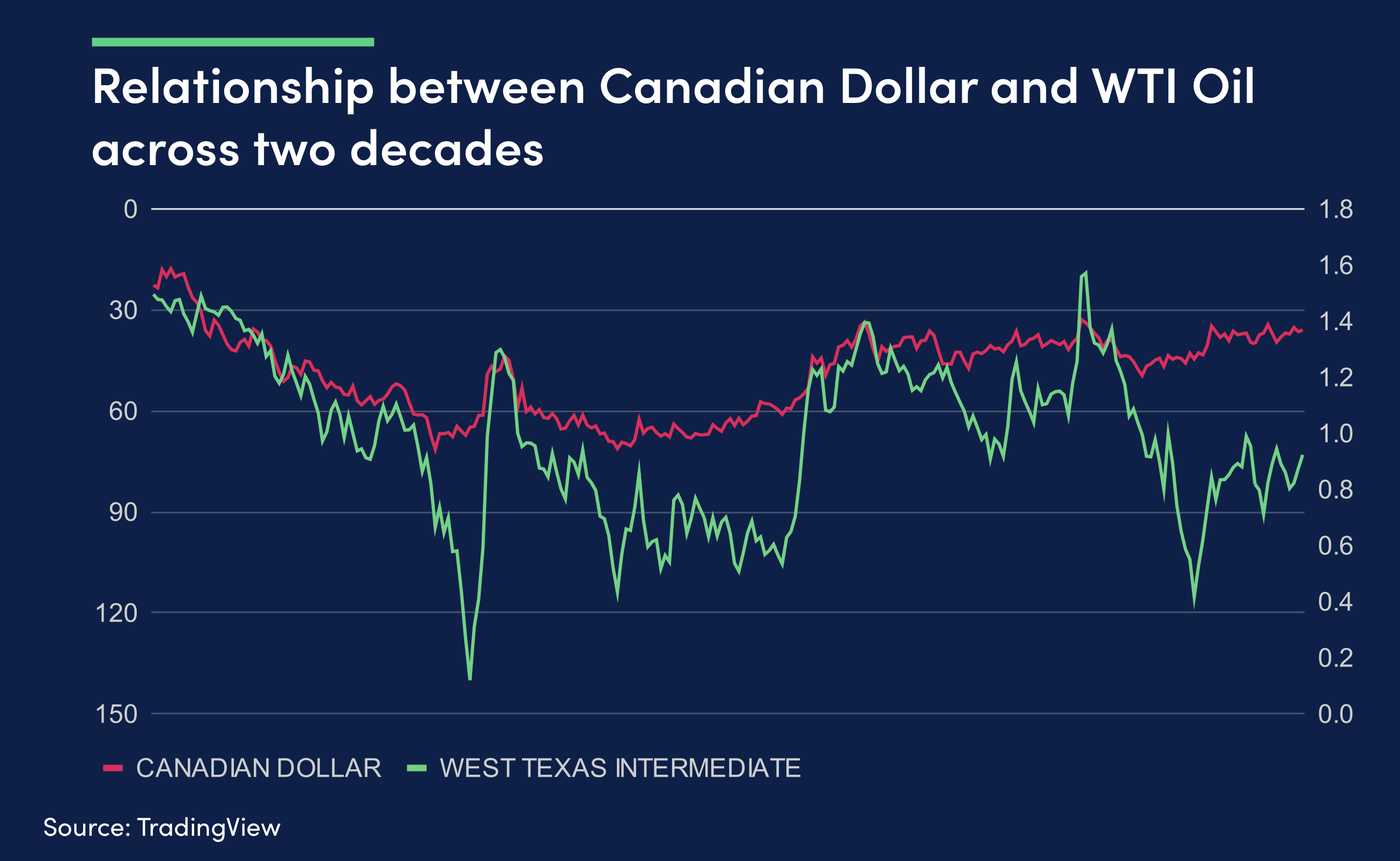
Canada’s economy is heavily reliant on exports, particularly on crude oil. Canada is the fifth largest oil producer in the world and the Canadian dollar and crude oil have historically been positively correlated. This means that the Canadian dollar often follows rises and declines in the price of crude oil and the Canadian dollar will be impacted by developments in Canada’s energy sector. The Canadian dollar is often referred to as a “commodity currency”, which underlines Canada’s heavy dependence on the export of natural resources.
Bank of Canada Interest Rate Policy
A country’s interest rate level is one of the most important factors in the value of a currency. The Bank of Canada announces its rate settings on fixed dates eight times a year and rate announcements are highly anticipated events. A hike in rates by the Bank of Canada will often boost the value of the Canadian dollar as higher rates attract foreign investment and thus more demand for the Canadian dollar. Conversely, if the Bank of Canada lowers rates, it often results in the weakening of the Canadian dollar.
However, Bank of Canada rate decisions are not the entire story. The value of the Canadian dollar will also depend on interest rate levels in the US and whether the US Federal Reserve raises or lowers interest rates. The US/Canada rate differential, which is the difference in interest rate levels between the two countries, is a key factor in the value of the Canadian dollar. For example, if US rates are higher than those in Canada, investors are more likely to invest in the US in order to earn higher returns and the influx of capital would boost the US dollar.
How Inflation Affects the Canadian Dollar
Inflation is closely connected to interest rate policy because the Bank of Canada will hike interest rates if inflation is too high and lower rates when inflation is low. Due to the close connection between inflation and interest rates, consumer price index (CPI) releases can have a significant impact on the movement of the Canadian dollar.
Canadian Economic Data
An important driver of the Canadian dollar is Canadian economic data. Key economic indicators include retail sales, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, and employment data. These indicators are usually released on a monthly basis and are considered market-movers as they often have an impact on the movement of the Canadian dollar.
As a general rule, if key indicators improve, it points to a stronger Canadian economy and the Canadian dollar will often rise as a result. Conversely, if an indicator declines, it indicates weaker economic activity and the Canadian dollar may decline in value.
Foreign Exchange Market Sentiment
Canada has a first-world economy and a stable political system, yet the Canadian dollar is viewed as a risk currency, primarily because the Canadian economy is heavily dependent on the export of commodities. Risk currencies perform well when the market sentiment is optimistic but may lose value during periods of market turbulence. In times of trouble, traders and investors will often flee to “safe haven” currencies, which include the US dollar, Japanese yen, and Swiss franc.
A geopolitical or economic crisis anywhere in the world is likely to result in market sentiment falling. Investors and traders usually respond by reducing risk which will mean selling risk currencies like the Canadian dollar in favor of a safe haven currency such as the US dollar. Conversely, if the markets are calm, traders and investors are more willing to take on risk and the Canadian dollar will appreciate in value as it is more in demand.
Political and Economic Stability in Canada
Foreign investors are always on the lookout to invest in countries with strong economies with low political and economic risk. Stable political conditions generally support a stronger currency. Canada is a peaceful and stable democracy and thus an attractive location for foreign investment. This has made the Canadian dollar a desired international currency.
US Dollar - Currency of the World
The US dollar is the most widely traded currency in the world, accounting for 90% of all forex trades. There are several reasons for the US dollar’s dominance in the forex markets. First, the US boasts the world’s largest economy which is the locomotive of international trade. Second, the US dollar is the world’s main ‘reserve currency’, which refers to funds held by central banks as part of their foreign exchange reserves and used by major financial institutions for international transactions. In essence, the US dollar is the “currency of the world”.
US - Canada Trading Relationship
In order to understand the relationship between the US dollar and the Canadian dollar, let’s first review the close trading relationship between the economies of Canada and the United States.
The US-Canada-Mexico free trade agreement (USMCA) has created the largest free trade zone in the world. The deal has been a tremendous success for Canada and has boosted the country’s economic growth. The USMCA has not, however, resulted in a stronger Canadian dollar. In fact, the Canadian dollar is considerably weaker than its US counterpart, which has boosted Canadian exports to the US and elsewhere due to the low value of the Canadian dollar.
Relationship between the Canadian and US Dollars
In the forex market, currencies are traded in pairs. The Canadian dollar/US dollar pair (USD/CAD) is one of the most actively traded currency pairs -it is the fifth most traded forex pair in the world and accounts for approximately 5% of all forex transactions. The USDCAD pair constitutes approximately 70-80% of all foreign exchange transactions involving the Canadian dollar.
The dominance of the USD dollar in forex trades involving the Canadian dollar is a reflection of the Canadian economy’s heavy dependence on its southern neighbor. It should be noted that references to the “Canadian dollar” usually mean USD/CAD, unless specified otherwise.
Canadian Dollar Forex Crosses
The US dollar is the most widely used currency for international trade as it is considered a trusted and stable medium of exchange. Currency crosses are pairs of currencies traded in forex that do not include the US dollar. The advantage of cross-currency transactions is that they allow currencies to be exchanged without having to first convert funds into US dollars. This is more efficient and saves transaction costs.
As we mentioned earlier, most forex trades involving the Canadian dollar are USD/CAD, but traders can also trade crosses in which the Canadian dollar is traded against other currencies, excluding the US dollar. Examples include EUR/CAD, GBP/CAD, and CAD/JPY.
Each of these currency pairs can be influenced by factors specific to both the Canadian economy and the economy of the other currency's country or region. For instance, CAD/JPY can be heavily impacted by oil prices since Japan is a major importer of Canadian oil. If, for instance, crude oil prices rise, it could provide a boost to CAD/JPY.
Relationship between the Canadian Dollar and China
China has the second largest economy in the world, behind only the United States. Let’s look at some key factors as to how China can impact the Canadian dollar.
Strength of China’s Economy
China is Canada’s second-largest export market after the United States and accounts for 4% of total Canadian exports. The main exports are crude oil and coal. The strength of the Chinese economy can affect the movement of the Canadian dollar. If China’s economy is in a slowdown, such as the present situation, there will be less demand for Canadian exports, which can result in a weaker Canadian dollar. Conversely, if China’s economy is expanding, demand will be greater for crude oil, which would be a positive development for the Canadian dollar.
China’s Demand for Crude Oil
China is the second largest consumer of crude oil after the United States and the largest importer of crude in the world. China accounts for about 25% of total global demand for crude and China’s oil consumption is expected to hit record highs this year, despite the economic slowdown. China’s strong demand for crude is an important factor in the high price of crude, which has helped boost the Canadian dollar.
Canadian Tariffs on Chinese Goods
Currently, Canada imposes small tariffs on Chinese goods, such as a 6% duty on Chinese automobiles. The US recently slapped higher tariffs on some Chinese products, and as a loyal ally and partner of the US, Canada may have to raise tariffs on China as well. If China retaliates against Canada, this would make Canadian exports to China more expensive and damage the export sector, which would push the Canadian dollar lower.
The Canadian economy is one of the most developed in the world and this has made the Canadian dollar a major currency that is in high demand by forex traders. Canada’s economy is highly dependent on crude oil exports and about 75% of all Canadian exports are sent to the United States. Thus, crude oil prices as well as the strength of the US dollar have a strong effect on the value of the Canadian dollar.
Disclaimer
This article is for general information purposes only, not to be considered a recommendation or financial advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Opinions are the author's; not necessarily that of OANDA Corporation or any of its affiliates, subsidiaries, officers or directors.
Leveraged trading in foreign currency contracts or other off-exchange products on margin carries a high level of risk and is not suitable for everyone. We advise you to carefully consider whether trading is appropriate for you in light of your personal circumstances. You may lose more than you invest. We recommend that you seek independent financial advice and ensure you fully understand the risks involved before trading.