Forex volatility: A comprehensive guide for Forex traders. Understand the dynamics of currency volatility, analyze market trends, and implement effective trading strategies to navigate the forex market
What is historical volatility
Historical volatility in forex trading refers to the degree of price fluctuations in a currency pair over a given time. It measures how much and how quickly the exchange rate of a currency pair changes. Various factors, such as economic news, political events, natural disasters, and market sentiment, can impact volatility. Traders often use volatility to assess the risk associated with a particular currency pair and to make trading decisions. Higher volatility generally indicates a more dynamic and potentially riskier trading environment, while lower volatility suggests a less volatile market. However, the risks remain anyway.
Market volatility can differ significantly between currency pairs. Some currency pairs are known for their high volatility, experiencing large and rapid price swings. Others are less volatile, with prices changing gradually over time.
Key drivers of currency pair volatility
- Economic strength: Currency pairs involving countries with solid and stable economies tend to be less volatile than those with weaker or more uncertain economies.
- Political stability: Political instability or uncertainty can lead to increased volatility in a currency pair.
- Interest rate differentials: Large differences between two countries can attract investors seeking higher yields, leading to increased volatility in the currency pair.
- Market liquidity: Currency pairs with high trading volumes and liquidity tend to be less volatile than those with lower volumes.
- Geopolitical events: Global events such as natural disasters, political tensions, or economic crises can cause increased volatility across currency markets, but the impact can vary depending on the specific currency pair and its relationship to the event.
Examples of volatility differences
- Major currency pairs: Pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD are typically more liquid and less volatile than emerging market currency pairs.
- Emerging market currencies: Currencies from developing economies, like the Mexican peso or the Turkish lira, can be more volatile due to political vulnerability, economic uncertainty, or lower liquidity (MXN, TRY).
- Commodity currencies: Currencies of countries heavily reliant on commodity exports (e.g., AUD, CAD, NZD, NOK) can be influenced by commodity price fluctuations, leading to increased volatility.
The role of volatility in currency pair selection and trading strategies
Understanding the typical volatility of different currency pairs is crucial for traders. It helps them assess risk, set appropriate stop-loss levels, and choose suitable trading strategies. For example, a trader looking for a high-frequency trading strategy that allows them to enter and exit the market more frequently, may opt for highly volatile currency pairs, which can provide more trading opportunities than less volatile ones. Another example can be a trader attempting to set a stop or a limit order. They may consider the average historical volatility along with their strategy parameters.
It is worth noting that volatility alone is not the only reason to choose which currency pair to trade. Traders must consider many other factors before selecting one. For example, although choosing a high-volatility currency pair may offer more trading opportunities, it may only be suitable for high-frequency trading strategies if the pair has enough liquidity.
Technical indicators for measuring volatility
- Average True Range (ATR): This indicator is a technical analysis tool used to measure market volatility. It focuses on the actual range of a price movement, which considers the current day's high and low and the previous day's closing price. The ATR then calculates an average of these true ranges over a specified period, typically 14 days. Traders can also customize the number of periods of their choice.
- Bollinger Bands: These consist of a moving average and an upper and lower band calculated based on standard deviation. The width of the bands expands or contracts based on market volatility. Wider bands indicate higher volatility, while narrower bands suggest lower volatility.
- Standard deviation: This statistical measure calculates the average price deviation from its mean over time. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility.
- Donchian channel: A technical indicator of three lines plotted on a price chart. The upper band represents the highest price the asset reached over a specified period (typically 20 periods), the lower Band represents the lowest price reached over the same period, and the middle Band represents the average of the upper and lower bands.
- Keltner channels: Similar to Bollinger Bands, they use Average True Range (ATR) instead of standard deviation.
- Volatility % (standard deviation of returns): This indicator measures the standard deviation of price changes over a specified period.
Analyzing volatility in Forex trading using TradingView
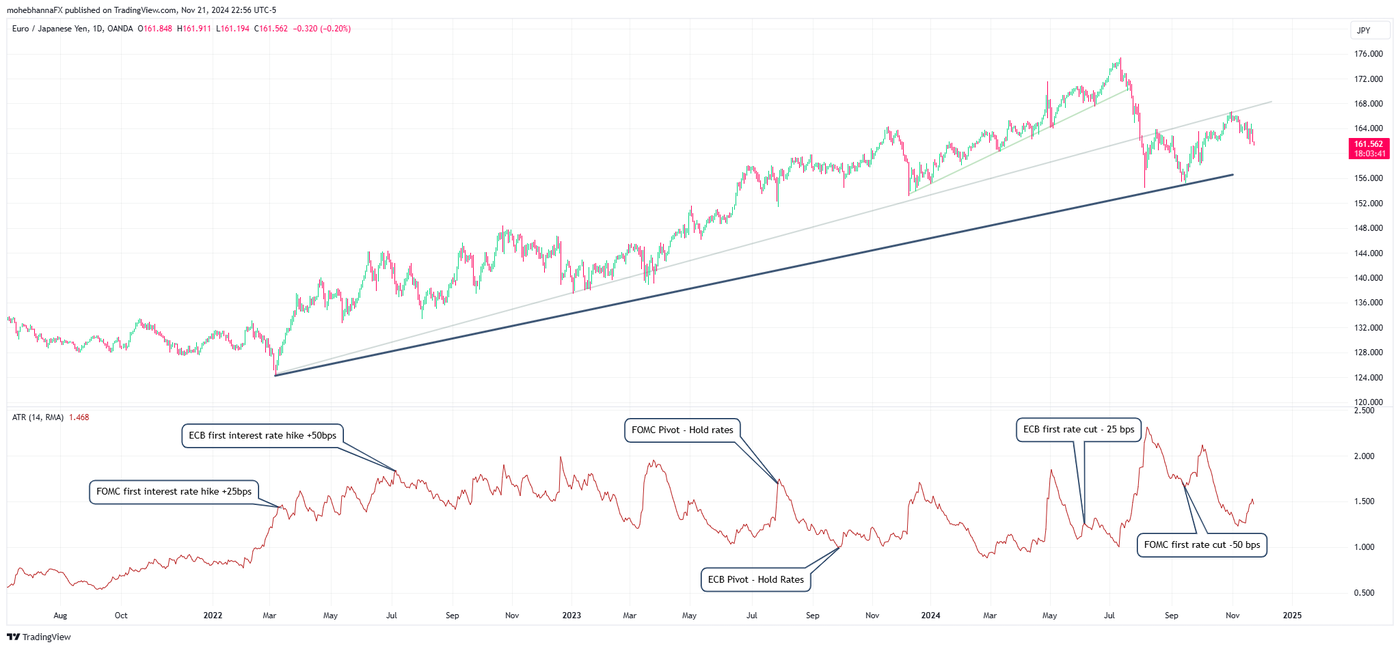
Visualization
The chart above highlights a few significant news events where volatility rose above average. It is for EUR/JPY, a currency pair that ranks high on volatility indexes. The Average True Range indicator is applied, and multiple major central bank events are marked on the chart.
In early 2022, major central banks worldwide, such as the Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank (ECB) used for our example here, confronted global high inflation rates not seen in more than 40 years. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) raised rates 11 times in 17 months and the ECB by 10 times in 16 months to bring inflation down. The central banks also had to maintain a balance, as raising rates can impact economic growth and the job markets. The uncertainty behind the central bank's anticipated decisions kept the markets on edge every time there was a central bank interest rate decision on the economic calendar, and there were many of them throughout the year.
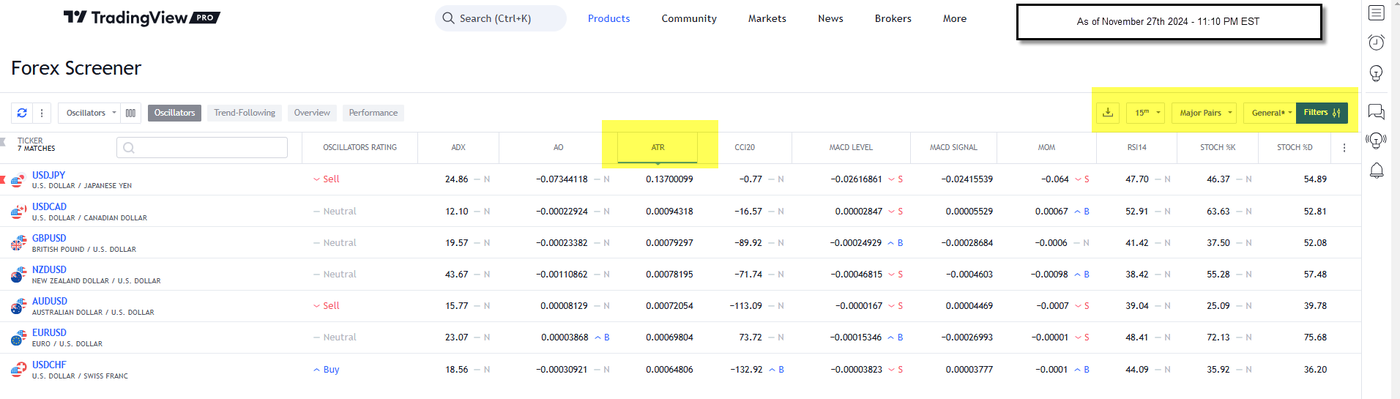
TradingView screener
The Forex screener tool on TradingView offers a combined overview of many technical tools and indicators on the same screen. It allows traders to view multiple indicator readings, which may help them make more informed decisions. Traders can customize the screener parameters according to their preferences.
To see how currency pairs volatility rank, follow the steps below:
- Click “Products” at the top of your TradingView screen, and choose "Screener". Select "Forex" as the instrument type.
- Add the "Volatility" filter and set your desired range.
- You can filter by other criteria, such as average daily range, trading volume, and economic news events.
- You can add these indicators to your charts and compare them across currency pairs.
Remember: Volatility is unpredictable and risky
- It is important to remember that volatility can be unpredictable, and success in trading volatile or non-volatile pairs is not guaranteed.
- It is important to remember that volatility can be unpredictable, and success in trading volatile or non-volatile pairs is not guaranteed.
- Be aware of the risks associated with trading volatile pairs. These pairs can experience significant and rapid price swings, which can lead to substantial losses.
- Research and develop a strategy appropriate for your risk tolerance and trading goals.
- Consider the time frame you are trading. Volatility can be higher in shorter time frames.
- Monitor the economic calendar for news and events that can impact volatility. Central bank announcements, inflation and employment indicators, political events, and natural disasters can all increase volatility in specific currency pairs.
Forex volatility: Takeaways
In summary, volatility is a double-edged sword in forex trading. It presents both opportunities and risks. Traders must understand the factors influencing volatility, use appropriate risk management strategies, and choose suitable tools and techniques to navigate the forex market successfully. While high volatility can offer increased trading opportunities, it also comes with greater risk. By carefully analyzing market conditions, employing proper risk management, and adapting to changing volatility levels, traders can increase their chances of success in the dynamic and ever-changing forex market.
This article is for general information purposes only, not to be considered a recommendation or financial advice. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Opinions are the author's; not necessarily that of OANDA Corporation or any of its affiliates, subsidiaries, officers or directors.
Leveraged trading in foreign currency contracts or other off-exchange products on margin carries a high level of risk and is not suitable for everyone. We advise you to carefully consider whether trading is appropriate for you in light of your personal circumstances. You may lose more than you invest. We recommend that you seek independent financial advice and ensure you fully understand the risks involved before trading.